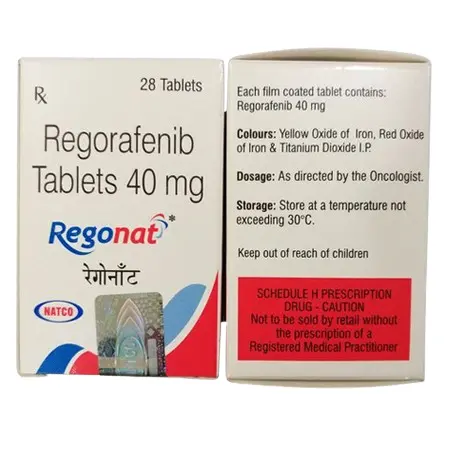
Regorafenib 40 mg Tablets: Complete Guide to Uses, Dosage, Side Effects & Cancer Treatment
What is Regorafenib 40 mg tablets?
Regorafenib is a medication used in the treatment of certain types of cancer, particularly advanced colorectal cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer) that cannot be surgically removed. It belongs to a class of drugs known as multikinase inhibitors, which work by blocking the activity of enzymes involved in cancer cell growth and progression. Regorafenib may help slow down the spread of cancer and prolong survival in patients with these types of cancer.
1. Composition
Each tablet contains:
- Regorafenib 40 mg (as regorafenib monohydrate)
Other ingredients (excipients) may include:
- Cellulose derivatives
- Magnesium stearate
- Hypromellose
- Iron oxide pigments (for coating)
2. Indications (Uses)
Regorafenib 40 mg is an oral targeted cancer therapy approved for the treatment of:
- Metastatic colorectal cancer in patients who have been previously treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, and with anti-VEGF and anti-EGFR therapies (if RAS wild-type).
- Advanced GIST after disease progression or intolerance to prior treatment with imatinib and sunitinib.
- Liver cancer previously treated with sorafenib.
Regorafenib is typically used in patients with advanced or metastatic disease after failure of other treatments.
3. Mechanism of Action
Regorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor that:
- Inhibits tumor angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels)
- Blocks tumor growth signals
- Targets several kinases involved in:
- VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3 (vascular endothelial growth)
- KIT (stem cell factor receptor)
- RET, RAF-1, BRAF (including mutated BRAF V600E)
- PDGFR and FGFR
This helps slow tumor growth and reduce metastasis.
4. Dosage and Administration
Typical Recommended Dose:
- 160 mg (four 40 mg tablets) once daily
- Schedule: 21 days on treatment, followed by 7 days off (28-day cycle)
Take with a low-fat meal to reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
Administration Instructions:
- Swallow tablets whole with water.
- Take at the same time each day.
- Do not crush or chew the tablets.
5. Side Effects
Very Common:
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Decreased appetite
- Hand-foot skin reaction (palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Mucosal inflammation
- Voice changes (dysphonia)
- Weight loss
- Rash
Less Common but Serious:
- Liver toxicity (can be life-threatening)
- Hemorrhage (bleeding risk)
- Infections
- Myocardial ischemia (heart-related issues)
- Delayed wound healing
Liver function tests (ALT, AST, bilirubin) should be closely monitored.
6. Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor liver function; discontinue if severe liver damage occurs.
- Hypertension: Monitor blood pressure; manage appropriately.
- Bleeding Risk: Caution in patients with active bleeding or coagulopathy.
- Cardiac Events: Risk of myocardial infarction and ischemia.
- Wound Healing Impairment: Stop treatment at least 2 weeks prior to surgery.
7. Drug Interactions
Avoid use with:
- Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin) – may reduce effectiveness
- CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) – may increase toxicity
- Anticoagulants – increased bleeding risk
8. Use in Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Not recommended. Can cause fetal harm.
- Breastfeeding: Avoid during and for 2 weeks after last dose.
- Pediatrics: Safety and efficacy not established.
- Geriatrics: Dose adjustment not usually necessary but monitor closely.
9. Storage Instructions
- Store at room temperature (20–25°C / 68–77°F)
- Protect from moisture and direct light
- Keep out of reach of children




Kevin (verified owner) –
Improved my overall wellness, fewer colds and viral infections.
John (verified owner) –
Viral Care keeps me healthy and energized all day.